Understanding the Emergence of a New Fatal H5N1 Avian Influenza Strain: Implications, Challenges, and Response Strategies
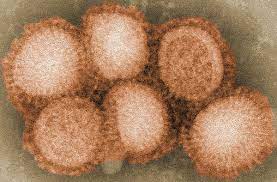
In recent years, the world has faced numerous challenges posed by infectious diseases, and among them, avian influenza remains a persistent threat with potentially devastating consequences. The emergence of a new fatal strain of H5N1 avian flu has raised concerns among public health officials, scientists, and the general population alike. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the characteristics of the new H5N1 strain, its potential impact on human and animal health, the challenges it presents, and the strategies for effective response and mitigation.
Understanding H5N1 Avian Influenza:
H5N1 avian influenza, also known as bird flu, is a highly pathogenic virus that primarily affects birds, particularly poultry, but has the potential to infect humans and other mammals. The virus belongs to the influenza A virus subtype H5N1 and can cause severe respiratory illness, organ failure, and death in infected individuals.
Characteristics of the New Fatal H5N1 Avian Flu Strain:
- Increased Virulence: The new strain of H5N1 avian flu is characterized by heightened virulence, meaning it has the ability to cause more severe disease and mortality in both birds and humans. This increased virulence poses a significant threat to poultry populations and raises concerns about potential outbreaks in domestic and wild bird populations.
- Enhanced Transmissibility: Preliminary studies suggest that the new H5N1 strain may exhibit enhanced transmissibility, meaning it can spread more easily between birds and potentially between humans. This increased transmissibility heightens the risk of widespread outbreaks and raises concerns about the potential for a global pandemic.
- Resistance to Antiviral Drugs: There are indications that the new H5N1 strain may exhibit resistance to certain antiviral drugs commonly used to treat influenza infections, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza). This resistance could limit the effectiveness of current treatment options and complicate efforts to control the spread of the virus.
- Genetic Mutations: Genetic analysis of the new H5N1 strain has revealed mutations in key viral proteins, including the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins, which play crucial roles in viral attachment, entry, and replication. These genetic mutations may contribute to the virus’s increased virulence and transmissibility.
Potential Impact on Human and Animal Health:
- Human Health: The emergence of a new fatal strain of H5N1 avian flu poses a significant threat to human health, as it has the potential to cause severe respiratory illness, pneumonia, and death in infected individuals. The increased virulence and potential for enhanced transmissibility raise concerns about the possibility of a global pandemic and the need for heightened surveillance, preparedness, and response measures.
- Animal Health: The new H5N1 strain also poses a serious threat to animal health, particularly poultry populations, which are highly susceptible to avian influenza. Outbreaks of the virus can lead to significant economic losses for the poultry industry, as well as pose risks to food security and livelihoods in affected regions.
Challenges and Response Strategies:
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Early detection and surveillance are critical for identifying outbreaks of the new H5N1 strain and implementing timely response measures. Enhanced surveillance efforts, including monitoring of bird populations, poultry farms, and human cases of influenza-like illness, can help detect and contain the spread of the virus.
- Vaccination and Control Measures: Vaccination remains an important tool for controlling the spread of avian influenza in poultry populations. Developing effective vaccines against the new H5N1 strain and implementing vaccination programs in high-risk areas can help reduce the incidence of the virus and mitigate its impact on animal health and welfare.
- Public Health Preparedness: Public health authorities must prioritize preparedness and response efforts to minimize the potential impact of the new H5N1 strain on human health. This includes ensuring access to medical care, antiviral drugs, and personal protective equipment for healthcare workers, as well as implementing measures to prevent the spread of the virus in communities.
- International Cooperation: Addressing the threat of the new H5N1 strain requires coordinated efforts and cooperation at the international level. Governments, public health organizations, and veterinary authorities must work together to share information, resources, and expertise, and coordinate response efforts to prevent the spread of the virus across borders.
Conclusion:
The emergence of a new fatal strain of H5N1 avian flu underscores the ongoing threat posed by infectious diseases and the need for vigilance, preparedness, and cooperation in addressing global health challenges. While the characteristics and potential impact of the new H5N1 strain raise concerns, effective surveillance, vaccination, and control measures can help mitigate the spread of the virus and protect human and animal health. By prioritizing collaboration, innovation, and solidarity, the international community can confront the threat of avian influenza and safeguard the health and well-being of populations around the world.





